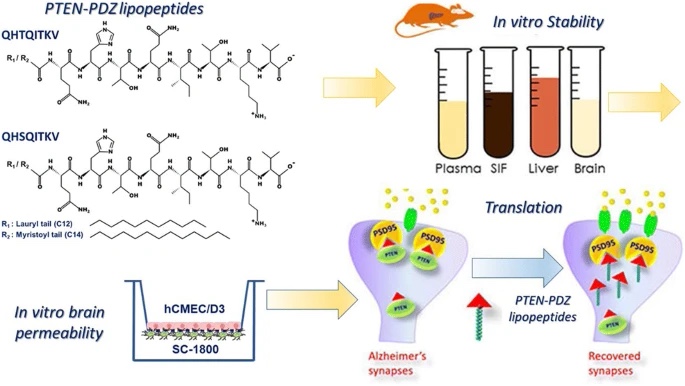
Amyloid β (Aβ) drives the accumulation of excess Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Deleted on Chromosome 10 (PTEN) at synapses, inducing synaptic depression and perturbing memory. This recruitment of PTEN to synapses in response to Aβ drives its interaction with PSD95/Disc large/Zonula occludens-1 (PDZ) proteins and, indeed, we previously showed that an oligo lipopeptide (PTEN-PDZ) capable of blocking such PTEN:PDZ interactions rescues the synaptic and cognitive deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Hence, the PTEN:PDZ interaction appears to be crucial for Aβ-induced synaptic and cognitive impairment. Here we have evaluated the feasibility of using PTEN-PDZ lipopeptides based on the human/mouse PTEN C-terminal sequence, testing their stability in biological fluids, their cytotoxicity, their ability to self-assemble and their in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Myristoyl or Lauryl tails were added to the peptides to enhance their cell permeability.